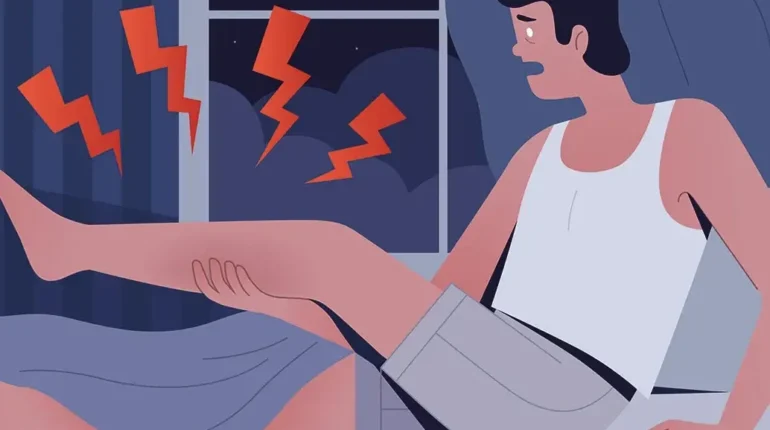
📌 This Silent Signal in Your Legs While You Sleep Could Mean Something Serious

Posted 1 December 2025 by: Admin
The Hidden Triggers Behind Your Nighttime Agony
Nighttime leg cramps strike suddenly, jolting you awake with sharp, unbearable pain that leaves you questioning what caused this nocturnal assault. The answer, more often than not, lies in an overlooked culprit: dehydration. When your body lacks sufficient fluids, muscles become dramatically more prone to spasms and involuntary contractions—the very mechanism that transforms a peaceful night into a painful ordeal.
This vulnerability intensifies for those who engage in intense physical activities or inhabit hot climates where fluid loss through sweating accelerates. The body’s demand for hydration skyrockets, yet many fail to replenish adequately during the day. By nightfall, muscle cells operate in a compromised state, their function deteriorating as dehydration deepens. The connection is physiological and direct: insufficient water intake starves muscles of the fluid environment they require for normal, controlled contractions.
What makes this trigger particularly insidious is its invisibility. You may not consciously realize you’re chronically under-hydrated until the cramps begin. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day—not just when thirst strikes—maintains the proper hydration necessary to keep muscles functioning smoothly. Yet dehydration represents only the first layer of this problem. Beneath it lies another critical factor that most people never suspect, one that operates silently within your very cells.
The Mineral Deficiency Crisis In Your Muscles
That silent factor is electrolyte imbalance—a nutritional crisis unfolding within your muscles as you sleep. Potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sodium aren’t merely minerals; they’re essential orchestrators of muscle function. These electrolytes govern muscle contraction and relaxation with precision. When they fall out of balance or become deficient, muscles lose their ability to respond appropriately, triggering abnormal contractions that jolt you awake in agony.
The vulnerability extends beyond casual negligence. People following restrictive diets, those taking certain medications, and individuals with kidney disease face the highest risk. Their bodies struggle to maintain proper electrolyte levels, creating an internal environment where cramping becomes inevitable. The mechanism is unforgiving: insufficient minerals mean muscles cannot perform their delicate dance of contraction and release.
The solution, however, remains within reach. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and nuts replenishes these critical minerals steadily. Potassium from bananas and sweet potatoes, calcium from yogurt and cheese, magnesium from almonds and spinach—these aren’t merely nutritional advice but muscular insurance. Yet even proper nutrition cannot protect against the third hidden danger threatening your nighttime comfort, one that attacks your muscles from an entirely different angle.
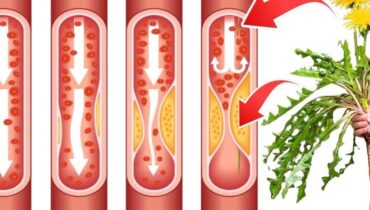
When Poor Circulation Starves Your Leg Muscles
That third hidden danger arrives silently through your circulatory system. Reduced blood flow to the legs deprives muscle tissues of oxygen and nutrients they desperately need to function properly. Without adequate circulation, muscles cannot receive the fuel required for smooth contraction and relaxation, forcing them into painful spasms that interrupt your sleep cycle.
Peripheral artery disease stands among the most significant culprits, progressively narrowing blood vessels and restricting oxygen delivery. Yet the danger extends to everyday habits as well. Prolonged sitting—whether at a desk, during long flights, or on the couch—compresses blood vessels and impairs circulation throughout your lower extremities. Over hours, this stagnation creates the perfect conditions for nighttime cramping.
The intervention is straightforward yet powerful. Regular exercise stimulates blood flow and strengthens cardiovascular health, ensuring your legs receive constant oxygen replenishment. Leg elevation before bed promotes venous return, allowing pooled blood to return efficiently to your heart. Even simple movements—walking, cycling, or stretching—can transform your circulatory efficiency and dramatically reduce cramping frequency. The muscles in your legs possess remarkable capacity for recovery once blood flow improves.
Yet circulation problems represent only part of the equation. Some cramps signal something far more serious beneath the surface, demanding your immediate attention.
Serious Warning Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
The distinction between manageable nighttime discomfort and a medical emergency often hinges on recognizing critical symptoms. When leg cramps persist despite lifestyle adjustments, or intensify in frequency and severity, they may signal underlying conditions demanding professional intervention. Nerve compression, diabetes, and thyroid disorders frequently manifest through nocturnal cramping as their initial warning sign—a message your body broadcasts before more serious complications emerge.
Pay particular attention to accompanying symptoms that elevate concern beyond ordinary muscle spasms. Swelling, numbness, or progressive weakness in the affected leg warrant immediate medical consultation. These red flags indicate your cramps transcend simple dehydration or electrolyte depletion. A healthcare provider can conduct proper diagnostics and identify whether peripheral neuropathy, circulatory disease, or metabolic dysfunction underlies your symptoms.
While awaiting professional assessment, proven prevention strategies offer meaningful relief. Gentle stretching before bed relaxes muscle tension and improves flexibility, creating conditions inhospitable to cramping. Massage increases localized blood circulation and soothes contracted fibers. Heat application relaxes muscles, while cold packs reduce inflammation when soreness persists. Equally critical: maintaining consistent hydration, consuming balanced nutrition rich in essential minerals, and avoiding excessive alcohol and caffeine—substances that aggravate both dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
The path forward combines vigilance with proactive care. Simple interventions prevent most cramps from disrupting your sleep, yet persistent or worsening episodes demand professional evaluation to ensure your overall health remains protected.