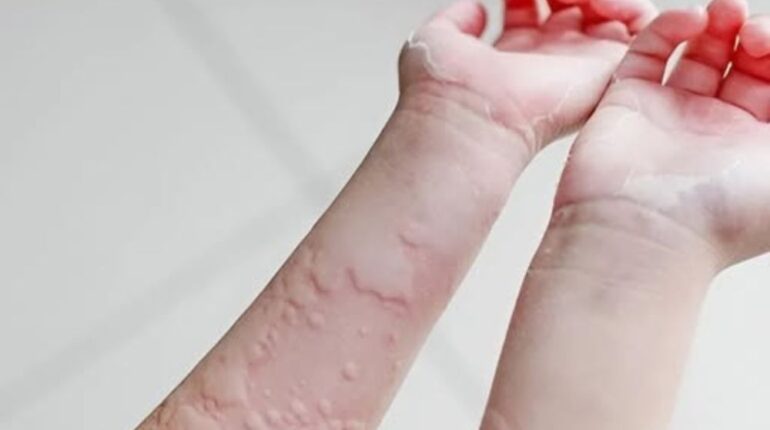
📌 Amazing Causes Of Hives Revealed
Posted 16 September 2025 by: Admin
Those itchy, red welts on your skin aren’t always about peanuts or pollen. From stress to sunlight, many unexpected factors can spark hives—understanding these triggers can help you prevent flare-ups and keep your skin calm.
Hives—also called urticaria—are sudden, itchy welts that can appear and disappear within hours. While food allergies or medications are well-known culprits, lesser-known causes can be just as responsible. Spotting these hidden triggers can make all the difference in managing outbreaks.
Let’s uncover 10 surprising reasons why hives might erupt—and how to handle them:
1. Stress and Anxiety
What’s Happening: Emotional stress triggers hormonal changes, increasing inflammation and **releasing histamine**, the same chemical behind allergic reactions.
How to Handle It:
Practice deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or mindfulness. Regular exercise and quality sleep can also lower stress-induced flare-ups.
2. Temperature Fluctuations
Sudden changes—like stepping from a hot shower into cool air or sweating after a workout—can cause cold or heat urticaria.
What You Can Do:
Dress in layers, avoid extreme temperatures, and shower with lukewarm water. Over-the-counter antihistamines may bring quick relief.
3. Skin Pressure or Tight Clothing
Why It Happens: Prolonged pressure—tight waistbands, sitting too long, or carrying heavy bags—can cause **pressure urticaria**.
Solutions:
Opt for loose-fitting, breathable clothing, shift positions often, and consider antihistamines for relief.
4. Unexpected Food Triggers
Besides common allergens like peanuts or shellfish, tomatoes, citrus, spicy foods, or fermented dishes can trigger reactions.
Next Steps:
Track symptoms in a food diary, and consult an allergist if patterns emerge.
5. Medications Not Typically Linked to Allergies
How It Happens: Even non-allergy-related drugs—like ibuprofen, antibiotics, or certain blood pressure medications—can provoke hives.
What To Do:
Review medications with your doctor, especially if hives follow a new prescription.
6. Viral or Chronic Illnesses
Why It Happens:
Infections like the common cold, mono, or hepatitis—or chronic issues such as thyroid disease—can spark outbreaks.
What Helps:
Treating the underlying condition often reduces hives.
7. Sunlight Sensitivity
Why It Happens: For people with **solar urticaria**, even short sun exposure can trigger welts.
Prevention Tips:
Wear UV-protective clothing, apply broad-spectrum sunscreen, and limit sun exposure during peak hours.
8. Hormonal Changes
Why It Happens: **Hormonal fluctuations**—during periods, pregnancy, or menopause—can heighten sensitivity.
What You Can Do:
Log your symptoms alongside your cycle and consult your healthcare provider about possible treatments or adjustments.
9. Water Contact (Yes, Really!)
What’s Going On: **Aquagenic urticaria** is a rare condition where hives develop after water contact—regardless of temperature.
How to Cope:
Minimize exposure, use gentle skin products, and seek medical advice for long-term strategies.
10. Hidden Allergens in Everyday Products
Why It Happens:
Fragrances or chemicals in soaps, lotions, shampoos, or detergents can provoke sensitive skin.
What to Try:
Switch to unscented, hypoallergenic products and patch-test new items on a small area first.
When Should You See a Doctor?
While hives are often harmless and fade on their own, seek help if:
- They persist longer than six weeks (chronic urticaria)
- You notice swelling of the lips, face, or throat (possible angioedema)
Though commonly linked to food or stings, hives can stem from many hidden causes. Identifying your triggers—and consulting a healthcare professional when needed—can help you manage flare-ups effectively.




















