📌 Flight attendants keep hands under thighs during takeoff to prevent injury: the body-restriction technique explained by safety protocols

Posted 14 December 2025 by: Admin
The Bracing Position Revealed: Why Flight Attendants Sit On Their Hands
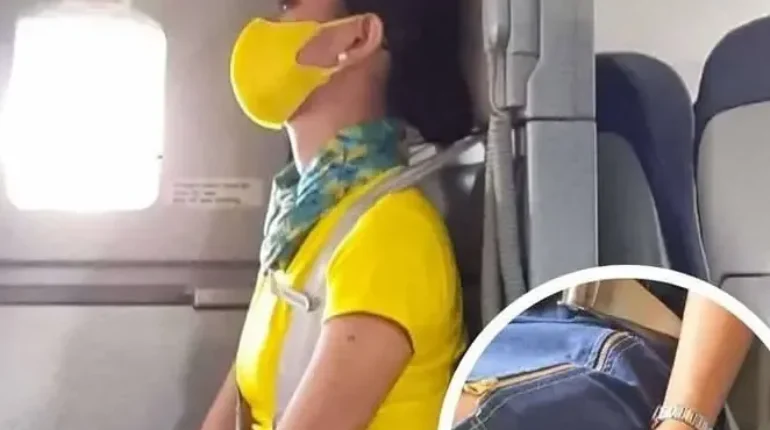
Next time you observe cabin crew settling into their jump seats before takeoff or landing, you’ll witness a peculiar ritual that serves far more purpose than comfort. A recent viral revelation from Cebu Pacific flight attendant Henny Lim has exposed what many passengers never understood: the deliberate positioning adopted by crew members during these critical flight phases.
In her TikTok video, Lim breaks down the exact mechanics of what aviation professionals call the bracing position. The protocol is remarkably specific: fastened seatbelts secured tightly, an upright posture maintained throughout, hands positioned firmly under the thighs with arms raised and thumbs tucked inward, and feet planted flat on the floor. This isn’t casual seating—it’s a choreographed safety stance executed during every single takeoff and landing across the aviation industry.
What makes this revelation particularly striking is how systematically it’s applied. Flight crews don’t adopt this posture sporadically or at their discretion. Instead, they follow this positioning as a mandatory protocol during the two most vulnerable phases of any flight. Lim’s behind-the-scenes exposure has sparked widespread curiosity among passengers who’ve unknowingly observed this behavior countless times without grasping its significance.
The specificity of every element—from thumb placement to foot positioning—suggests this isn’t mere habit or preference. Each component serves a deliberate biomechanical function, hinting at deeper safety considerations that transcend simple comfort or protocol adherence. The question naturally emerges: why would aviation authorities mandate such precise positioning if it didn’t address genuine emergency scenarios?
The Life-Saving Science Behind The Posture
Behind every precisely orchestrated movement lies uncompromising biomechanical logic. The bracing position isn’t arbitrary choreography—it represents decades of aviation safety research distilled into actionable protocol. When Lim describes how the positioning restricts body movement to minimize injury probability, she’s revealing the core principle that underpins emergency response across the global aviation industry.
During unexpected impact scenarios, human bodies become subject to violent forces. The bracing position intercepts this reality by anchoring the torso and limbs in configurations that fundamentally alter injury trajectories. By sitting upright with hands secured beneath the thighs, crew members eliminate the reflexive flailing that typically compounds trauma during collisions. The tucked thumbs and flat feet aren’t decorative details—they’re strategic constraints that stabilize the spine and lower extremities against impact shock.
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) confirms this scientific foundation through official documentation. According to FAA safety protocols, the bracing position serves two primary functions: reducing flailing and limiting secondary impact. The first objective prevents the uncontrolled limb movements that amplify injuries; the second mitigates the cascading trauma when bodies collide with overhead compartments, armrests, or surrounding structures. This dual-purpose framework reveals why every element of Henny Lim’s breakdown matters so intensely.
What transforms this from mere theory into operational reality is systematic application. Every airline globally enforces identical positioning protocols, suggesting convergence around shared scientific evidence rather than coincidental practice. This uniformity across carriers indicates that aviation authorities have collectively determined this posture offers demonstrable protection—knowledge that remains virtually invisible to passengers watching their cabin crew settle into these positions during routine flight sequences.
The Silent Review: Mental Preparation Passengers Never See
While the physical bracing position anchors crew members against impact forces, an equally critical safeguard unfolds entirely beneath the surface. During every takeoff and landing, flight attendants engage in what the industry calls the “silent review”—a mental protocol that transforms routine flight phases into active emergency preparedness sessions.
This cognitive exercise operates in parallel with the physical positioning Lim described. As crew members settle into their jump seats with hands secured beneath their thighs, their minds execute a systematic mental map. They mentally locate emergency equipment throughout the cabin, review door operation procedures, memorize commands they’d execute under duress, and assess visual cues beyond the aircraft windows. The process requires no audible communication; it’s a self-directed inventory that prepares them for scenarios most passengers never contemplate.
What distinguishes this protocol from casual awareness is its mandatory, choreographed nature. The silent review isn’t optional reflection—it’s a formal safety procedure mandated across aviation operations. Every takeoff and landing triggers this mental activation, creating muscle memory through repetition. Over a career spanning thousands of flights, flight attendants internalize emergency procedures until their responses become instinctive rather than deliberative.
This convergence of physical restraint and mental preparation reveals aviation’s layered safety architecture. The visible bracing position represents only the exterior dimension of emergency readiness. The silent review demonstrates that genuine safety preparation demands cognitive engagement alongside physical protocol, ensuring crew members arrive at crisis moments already mentally oriented toward decisive action.
Flight Attendants Break The Silence: TikTok As Aviation Education Platform
Beyond the procedural safeguards embedded within aviation protocols lies a modern shift in how the industry communicates directly with passengers. Flight attendants increasingly leverage social media to demystify their profession, transforming platforms like TikTok into unexpected channels for safety education and professional insight.
Henny Lim’s viral revelation exemplifies this trend. By exposing the mechanics of the bracing position to her audience, she answered a question countless passengers silently harbored during every takeoff and landing. Yet she represents merely one voice in a growing chorus of cabin crew members using digital platforms to bridge the knowledge gap between industry practice and public understanding.
Flight attendant Esther Sturrus, commanding 223,800 followers on social media, extends this educational mission beyond safety protocols. Sturrus defines the ideal passenger through a lens passengers themselves rarely consider: those who are “polite and friendly” combined with genuine courtesy and engaging in meaningful conversation. This characterization reveals an often-overlooked dimension of air travel—that crew member satisfaction correlates directly with passenger behavior and mutual respect.
Sturrus’s content spans practical domains as well, addressing concerns travellers frequently confront. Whether explaining how to maintain fresh clothing during extended journeys or offering etiquette guidance, she equips passengers with intelligence traditionally confined to industry insiders. This democratization of aviation knowledge transforms crew members from faceless service providers into accessible educators.
The phenomenon reflects a broader recognition: informed passengers become safer, more respectful passengers. By volunteering their expertise on social platforms, flight attendants don’t simply satisfy curiosity—they cultivate a traveling public more aligned with the safety culture that protects everyone aboard.